New versions of malware are appearing on the Internet, that – installed on the computer of the user logging into the internet service of PKO Bank Polski – can be used by criminals to execute unauthorised transactions from the accounts of customers of the bank.
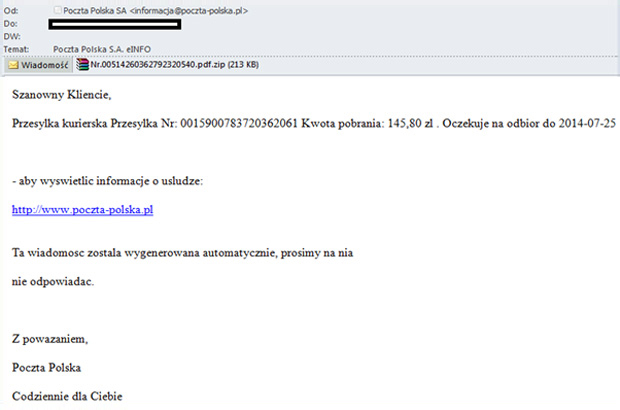
Devices with which users connect to the Internet are usually infected as a result of opening attachments to fraudulent e-mails in which hackers impersonate companies providing telecommunications services and other and inform about the necessity of alleged payments, payment for an invoice for the phone or for awaiting courier delivery. Using the trust of the message recipient to the commonly known company and their concern with the necessity to make payment, criminals induce them to open an attachment to the message containing allegedly details of the overdue payment.
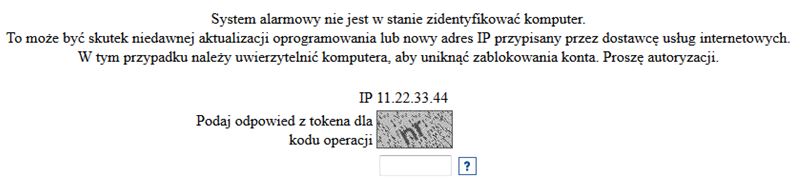
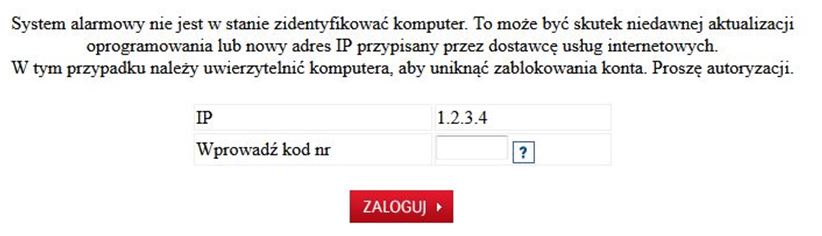
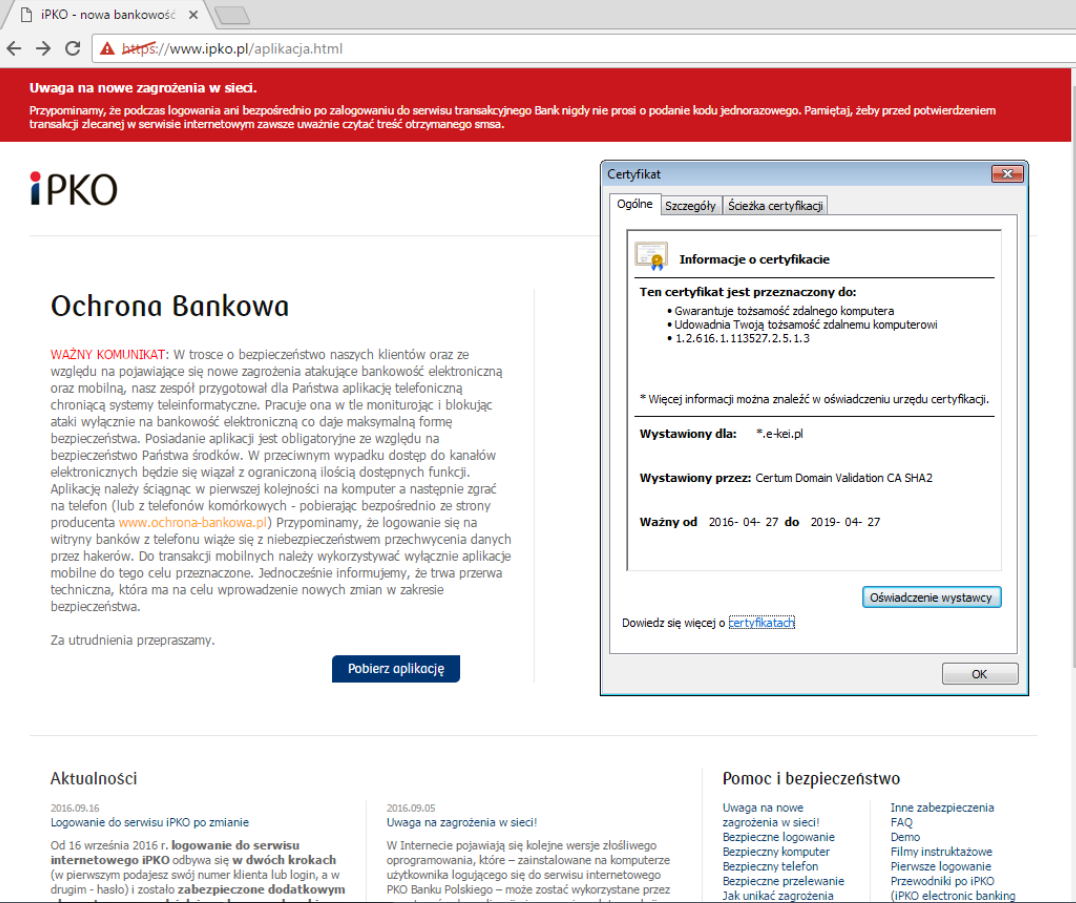
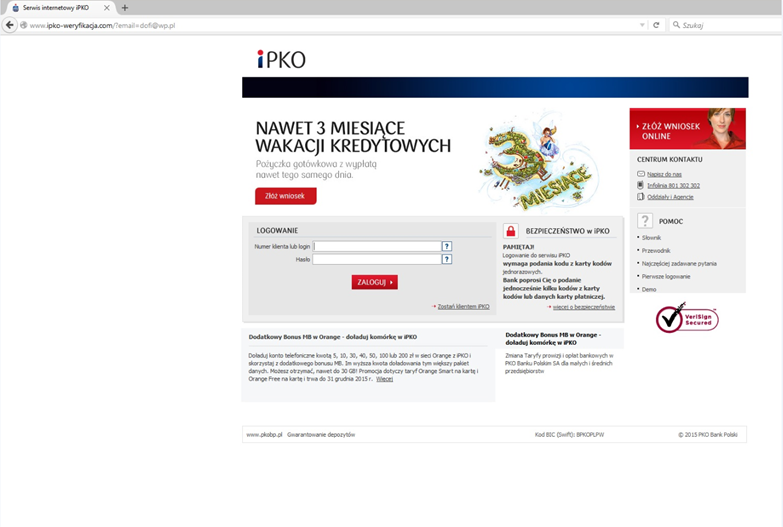
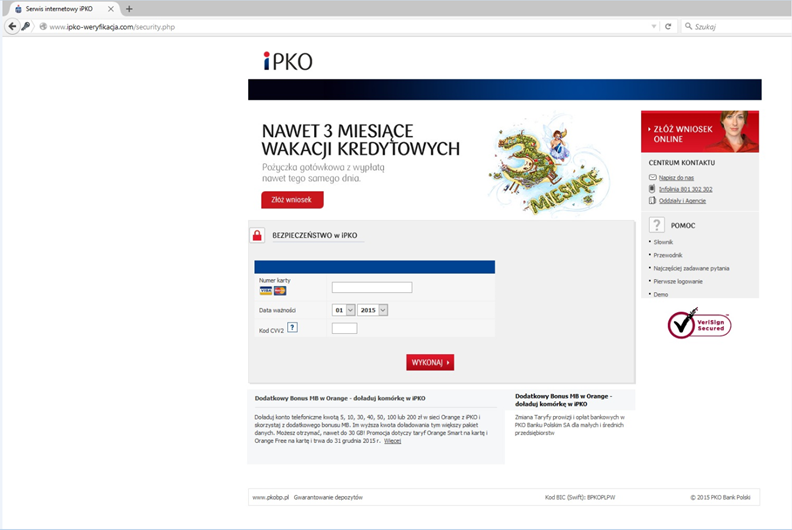
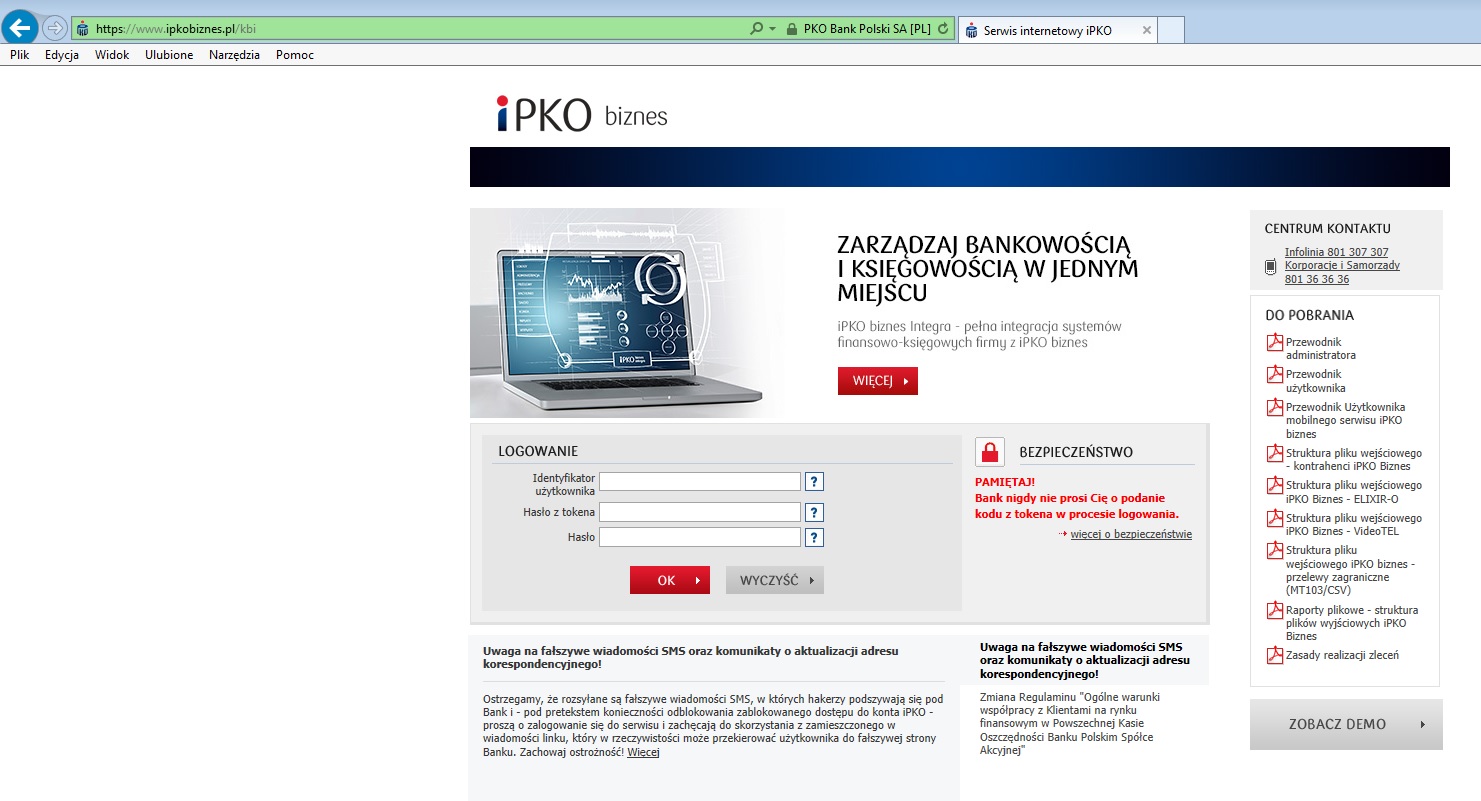
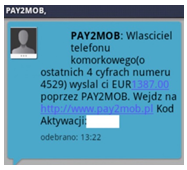
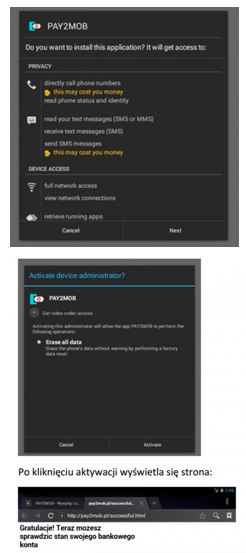
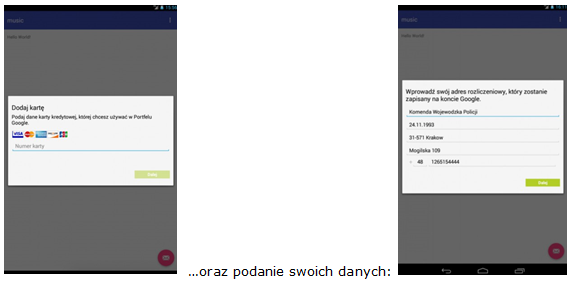
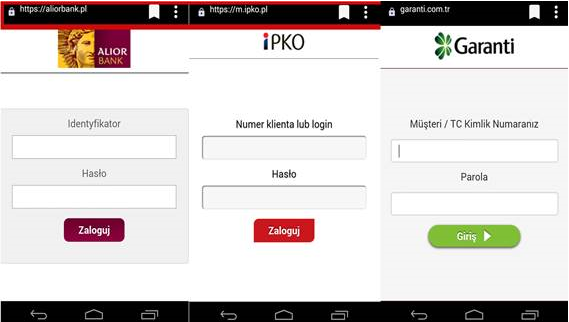
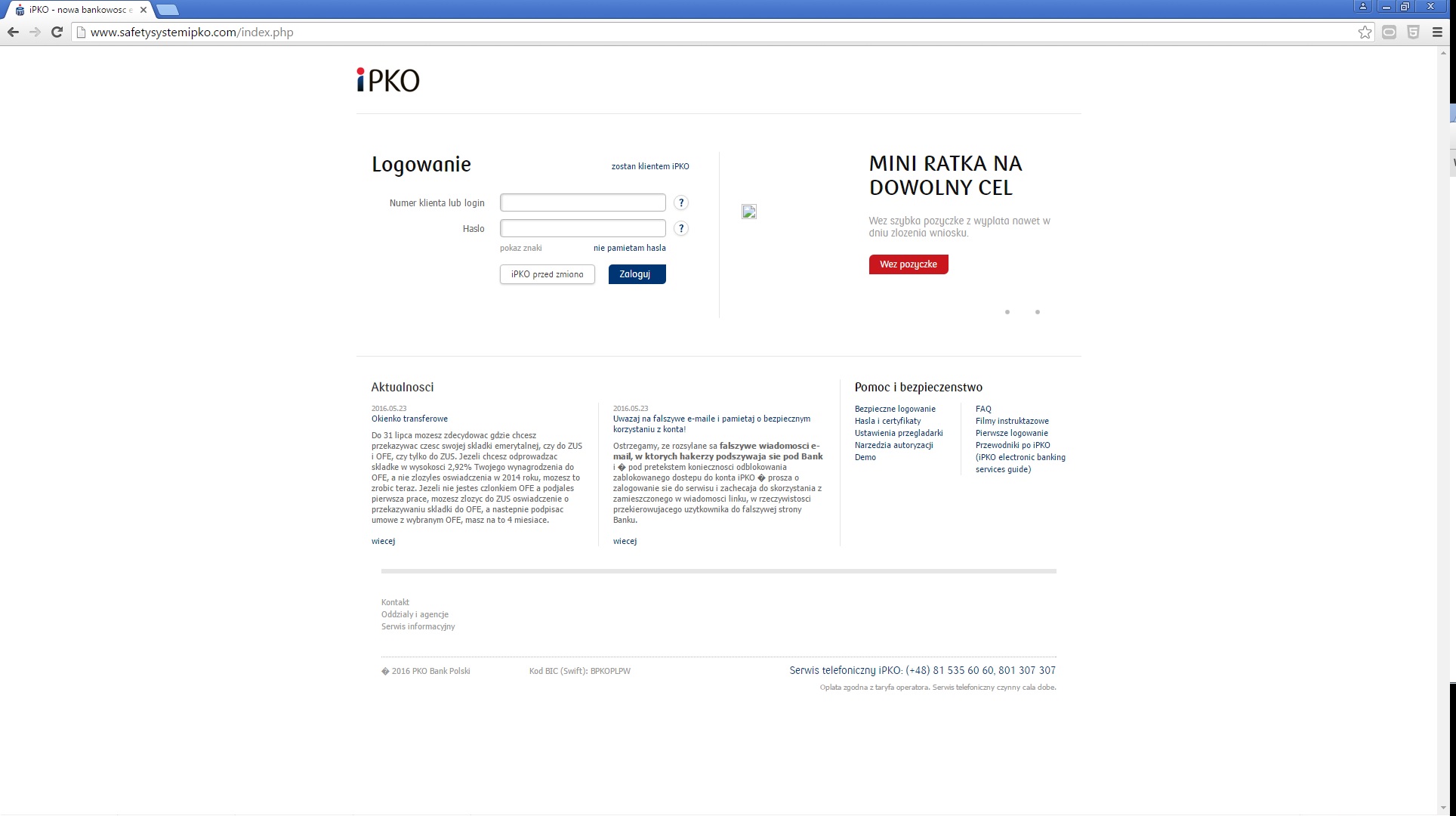
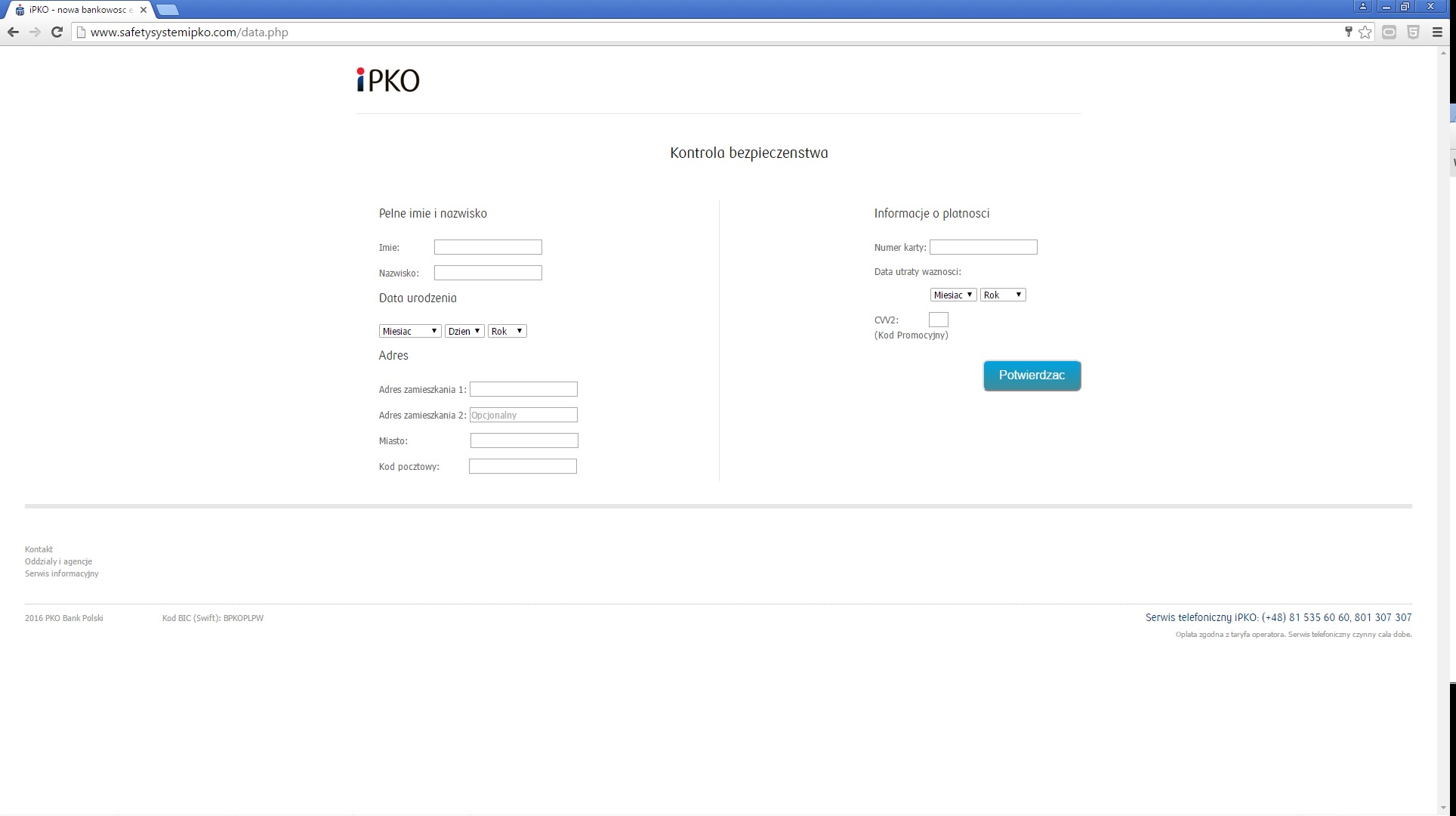
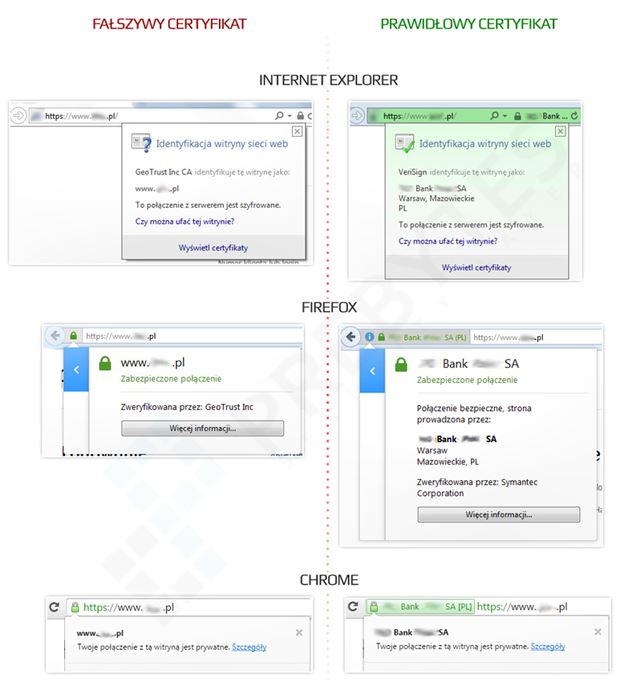
However, in reality opening of the attachment infects the computer on which the attachment is being opened with a dangerous virus, allowing the theft of confidential customer data (data to log into the www service), and above all displaying messages issued by criminals when logging into the electronic banking. As a result, the customer may yield to requests to enter codes from a one-time codes card, SMS code or code of the token, unknowingly authorising in this way criminal transfer from their own account.
In the same way attachments to fraudulent e-mails operate, informing about the alleged non-delivery of an e-mail to the recipient.
In the case of using the internet service of the bank from the virus-infected computer, immediately after logging in, i.e. after entering the customer number and access password, the user can be requested to provide a one-time code from the authorisation tool, although in a given moment they do not submit any instruction from their account. The entered code can then be used by criminals (in a manner invisible to the customer) to execute a transfer or define a new payee template to a specified target account. On the basis of such created payment template criminals may order transfers without the necessity to provide subsequent authorisation codes.
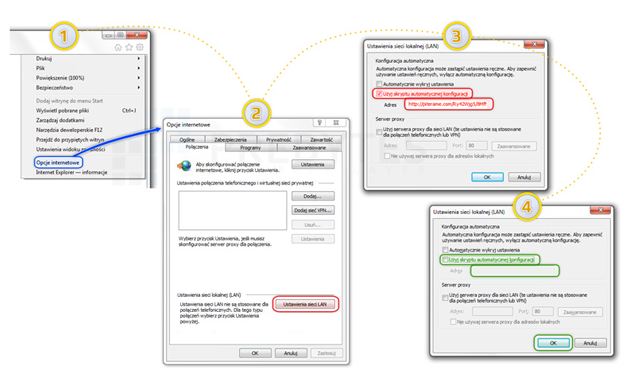
A computer or phone can also be infected as a result of installing the software from unknown sources on the device.
In order to avoid the above threats, learn the basic rules of the safe use of electronic banking.